“What honour is left to us when we have to take orders from a handful of traders who have not yet learned to wash their bottoms?” This was a remark made by a Mughal official, Narayan Singh in 1765, shortly after British officials were granted the rights to collect taxes from Indians.
India was always a global centre of textiles, crafts, literature, science, medicine, technology and riches. When the British came to India, they had to justify their rule over such proud people. So, the British did something no other foreign invaders had done before- they struck at our education system.

During the Revolt of 1857, Indians fought against the British and nearly rid the country of the colonisers. The Sepoys, fought gallantly, and Hindus and Muslims fought under each other’s commands and died for one another. This Revolt rattled the British administration, who realised that a united India cannot be looted peacefully.They introduced a system of education, which subsequently stripped our forefathers of their pride in their culture. They systematically destroyed Indian education and replaced it with one that portrayed Victorian lifestyle as superior, though it was not so.
For millennia, Indian society was the most pluralistic, the most open-minded one in the world. Christianity flourished in India centuries before it was introduced in Europe. Jews sought refuge in India, when they were being persecuted everywhere else in the world in the Ancient and Medieval times (However, after the formation of the State of Israel, many Jews returned to their ancient homeland). Zoroastrians fled Persia to avoid oppression to find peace in India. But none of this is taught in Indian textbooks.
The British created a number of falsehoods, which served the purpose of pitting one group against another.
The Aryan Invasion Theory is an exemplification of British propaganda. After translating ancient Indian texts like the Vedas, which refer to the Sun as a ball of burning fire, has details and references to black holes(I am just as perplexed as you are), states that the world is a sphere(the Sanskrit word for geography is भूगोलविज्ञान, where भू means Earth, गोल means round, or spherical and विज्ञान translates to knowledge), has detailed procedures of modern medical practices, they were befuddled to find out that Indians knew for millennia what Europe was just discovering.
But just then, they found out that an ancient group called the Aryans wrote these texts and the Aryans came from Europe (how convenient!) This theory was, in fact concocted by the Europeans to restore their self esteem by justifying that Ancient Indian texts were of European origin. Furthermore, this theory went on to say that ‘South Indians’ and ‘North Indians’ (terms created by the British to refer to us as contrasting peoples) are ethnically dissimilar, as North Indians are the ‘Descendants of the Aryans’ and South Indians are an entirely separate race.
This theory makes no sense whatsoever and has even been proved false by many researchers. In fact, in recent findings at the Harappan site at Rakhigarhi in Haryana, in which samples of remains of the residents were unearthed and studied, there were neither any traces of a mass killing of people, as the Aryan Theory suggested, nor any trace of Central Asian or European DNA, completely refuting any ‘Aryan’ migration or invasion. This is just one example of what the British did to justify their rule to reassure to themselves that they were not inferior to Indians.
Mathematics in India had been, for millennia, had been of a higher order when compared to its Western and Eastern counterparts(save perhaps China). A few facts to support this statement have been compiled below.
What is now known as the Hindu-Arabic numeral system(0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9) is a corruption of the Indian Devanagari numeral system(० १ २ ३ ४ ५ ६ ७ ८ ९), adopted by the Arabs who exposed it to the Europeans, hence the name. It was merely carried to Europe by the intermediary Arabs, who formed the trade link between Europe and India. It is a well-known fact that zero was invented in India by Aryabhatta more than one and a half millennia ago, as was the decimal system that is now used by the world, but few are aware about the fact that Algebra also owes its existence to Ancient Indian mathematicians. During the Islamic Golden Age, Persian Al-Khwarizmi expatiated on several concepts, borrowed from Indian mathematicians(yeez Arabs and Persians are good at this ‘borrowing’ business), thus laying the basis of modern algebra.
Mādhavā, Āryabhatta, Brahmaguptā and many more ancient Indian Mathematicians developed and advanced trigonometry. The earliest mentions of the sin-cosine functions have been found in the Siddhantas and Āryabhatya(Āryabhatta’s book). Jya and Koti-Jya, as they were called then, after being translated into Arabic and subsequently mistranslated into Latin started to be called sine and cosine by Mathematicians. Pi(yes, even Pi) was calculated, almost correct to 4 digits, by Āryabhatta (62832/20000 or 3.1416).

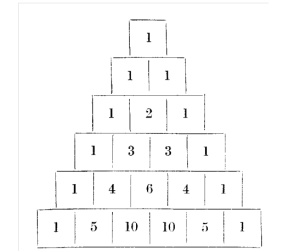
Pascal’s Triangle, as it is called in the Indian curriculum was first discovered in India by Pingāla in the 2nd century BC and was called Meru-Prastāra, or Meru Tabulation, but our textbooks assert its French origin, even though Blaise Pascal ‘discovered’ his triangle nearly 2 millennia after his Indian counterparts did.
None of the aforementioned facts can be seen anywhere in Indian textbooks.
Slowly, as more and more Indians started attending English schools in colonial times, they became English in taste, and remained Indians only in blood and colour(pat yourself in the back if you got the reference). These Anglicised Indians had little knowledge about their own culture and history. Shortly after Independence, it was these Indians who were tasked with formulating an education system. For that time, they did the best they could, drawing from their own education and the education system left behind by the European invaders, but now, even though we have made headway in rediscovering our heritage, which our colonisers have tried to cover up for a century, our education system, which millions of Indians study from today, is still based on the Imperial British content and Victorian culture and values.
The legacy of British colonialism lives on in our own textbooks, which obfuscate India’s contribution to maths, science and medicine. Our education system must be reformed to make it inclusive, and teach us about Indian culture and Indian values.
-Ishaan Mishra

4 replies on “The ‘Indian’ Education System”
Love the passion behind your writing. Very informative too. Keep writing!
LikeLike
Hey! I love your style of writing and really enjoy your personal comments in the brackets. Reading this really made my day and gave me something to think about. Good job Ishaan!
LikeLike
Keep it your view and sight of ancient glory , those are not touched our vision!
LikeLike
Very well written with facts and fluidic style of writing….keep it up!
LikeLike